Taro实现 h5,小程序(滚动吸附刻度尺功能)
2025-08-07
最近在做小程序的时候遇到了需求,需要实现一个支持滑动,带有惯性吸附等功能的刻度尺效果
大概效果如图所示
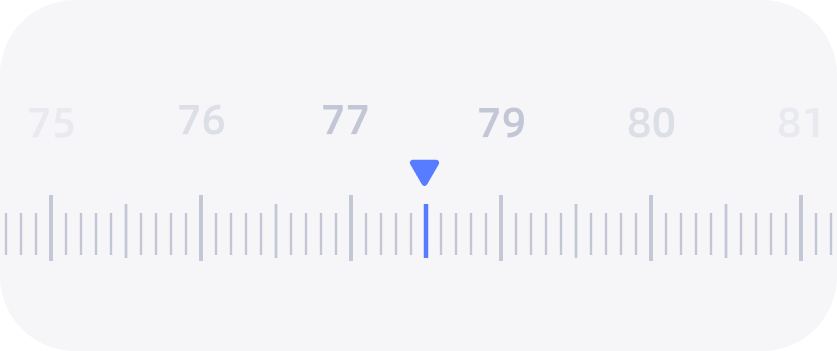
话不多说,直接上代码吧
- 首先定义这个组件的props,因为是刻度,所以需要一个范围区间,然后我们要支持水平和垂直两种状态,适用于身高和体重两种情况。
interface ScaleRulerProps {
minScale?: number; // 最小值
maxScale?: number; // 最大值
containerSize?: number; // 容器宽度
majorTickSize?: number; // 大刻度宽度(整数)
minorTickSize?: number; // 小刻度宽度(小数)
onChange?: (value: number) => void; // 滚动结束时触发的回调
currentValue?: number; // 当前刻度值
direction?: "horizontal" | "vertical"; // 刻度尺方向,默认为水平
}- 因为涉及到滚动吸附到精确的刻度,所以我们要计算一共有多少刻度,并且计算刻度宽度,同时要记录每一个刻度的相对位置,这里我们默认每个小刻度都是 0.1
// 计算总刻度数
const items = Array.from({length: (maxScale - minScale) * 10 + 1}, (_, i) =>
parseFloat((minScale + i / 10).toFixed(1)),
);
// 计算刻度宽度
const tickWidths = useMemo(
() =>
items.map((item) =>
Number.isInteger(item) ? majorTickSize : minorTickSize,
),
[items, majorTickSize, minorTickSize],
);
// 计算内容总宽度(需要将 gap 的宽度也计算进去)
const contentSize = useMemo(
() => tickWidths.reduce((acc, w) => acc + w, 0) + (items.length - 1) * gap,
[tickWidths, items.length],
);
// 记录每个刻度的位置
const tickPositions = useMemo(() => {
let position = 0;
const initialOffset = containerSize / 2 - contentSize / 2;
return items.map((item, index) => {
const currentPosition = position;
const tickWidth = tickWidths[index];
// 计算刻度中心在容器坐标系中的位置
const tickCenterInContainer =
initialOffset + currentPosition + tickWidth / 2;
// 更新位置用于下一个刻度
position += tickWidth + (index < items.length - 1 ? gap : 0); // 加上gap
return tickCenterInContainer;
});
}, [items, tickWidths, containerSize, contentSize]);- 限制滚动的区域
// 可滑动的区域限制
const halfContentSize = contentSize / 2;
const minScrollPosition = -halfContentSize; // 最左边:向右滑动到内容宽度的一半
const maxScrollPosition = halfContentSize; // 最右边:向左滑动到内容宽度的一半- 接下来要根据 touchStart,touchMove 等事件来配合处理
// 触摸开始
const handleTouchStart = (e: ITouchEvent) => {
setIsDragging(true);
setLastTouchPosition(
isHorizontal ? e.touches[0].clientX : e.touches[0].clientY,
);
velocityRef.current = 0;
if (animationRef.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(animationRef.current);
}
};
// 触摸移动
const handleTouchMove = throttle((e: ITouchEvent) => {
if (!isDragging) return;
const currentPosition = isHorizontal
? e.touches[0].clientX
: e.touches[0].clientY;
// 滚动距离
const delta = lastTouchPosition - currentPosition;
setScrollPosition((prev) => {
const rawNext = prev + delta;
// 限制滚动范围
const clampedNext = clampScrollPosition(rawNext);
return clampedNext;
});
const maxVelocity = 40;
const limitedVelocity =
Math.sign(delta) * Math.min(Math.abs(delta * 1.8), maxVelocity);
velocityRef.current = limitedVelocity;
setLastTouchPosition(currentPosition);
}, 16.7);
// 触摸结束
const handleTouchEnd = useCallback(() => {
setIsDragging(false);
// 惯性吸附
if (Math.abs(velocityRef.current) > 1) {
// 速度较大时开始惯性滚动
animationRef.current = requestAnimationFrame(inertiaScroll);
} else {
// 速度较小时直接吸附
setScrollPosition((prev) => snapToNearestTick(prev));
}
}, [velocityRef.current]);- 实现自动吸附和寻找最近刻度
// 计算最接近中心指示器的刻度索引
const findNearestTickIndex = (currentScrollPosition: number) => {
if (!tickPositions || tickPositions.length === 0) return 0;
const centerIndicatorPos = containerSize / 2;
const centerInContentCoords = centerIndicatorPos + currentScrollPosition;
let nearestIndex = 0;
let minDistance = Math.abs(tickPositions[0] - centerInContentCoords);
for (let i = 1; i < tickPositions.length; i++) {
const distance = Math.abs(tickPositions[i] - centerInContentCoords);
if (distance < minDistance) {
minDistance = distance;
nearestIndex = i;
}
}
return nearestIndex;
};
// 吸附到最近的刻度
const snapToNearestTick = useCallback(
(currentScrollPosition: number) => {
const nearestIndex = findNearestTickIndex(currentScrollPosition);
const targetTickPos = tickPositions[nearestIndex];
const centerIndicatorPos = containerSize / 2;
const targetScrollPosition = targetTickPos - centerIndicatorPos;
// 限制在边界内
return clampScrollPosition(targetScrollPosition);
},
[findNearestTickIndex, tickPositions, containerSize, clampScrollPosition],
);
// 惯性滚动
const inertiaScroll = useCallback(() => {
const currentVelocity = velocityRef.current;
if (Math.abs(currentVelocity) < 0.5) {
// 速度很小时停止惯性滚动,开始吸附
setScrollPosition((prev) => snapToNearestTick(prev));
velocityRef.current = 0;
return;
}
setScrollPosition((prev) => {
// 根据速度动态调整每帧移动距离
let frameMove = currentVelocity;
// 限制最大移动速度
const maxSpeed = 40;
if (Math.abs(frameMove) > maxSpeed) {
frameMove = Math.sign(frameMove) * maxSpeed;
}
const newScrollPosition = clampScrollPosition(prev + frameMove);
// 如果达到边界,减少速度
if (newScrollPosition === prev) {
velocityRef.current = 0;
return prev;
}
return newScrollPosition;
});
const deceleration = 0.96;
velocityRef.current *= deceleration;
animationRef.current = requestAnimationFrame(inertiaScroll);
}, [velocityRef.current, clampScrollPosition, snapToNearestTick]);- UI实现
<View className="h-full w-full flex items-center justify-center overflow-hidden">
<View
className={clsx(
"relative overflow-hidden bg-[#f5f5f8] rounded-2xl mt-2 flex",
isHorizontal
? "flex-row h-28 items-end justify-center py-3 px-2"
: "w-28 items-center justify-end px-3 py-2",
)}
style={{
width: isHorizontal ? `${containerSize}px` : "",
height: isHorizontal ? "" : `${containerSize}px`,
}}
>
<View
className="rule flex items-center"
onTouchStart={handleTouchStart}
onTouchMove={handleTouchMove}
onTouchEnd={handleTouchEnd}
catchMove
style={{
gap: `${gap}px`,
transform: isHorizontal
? `translateX(${-scrollPosition}px)`
: `translateY(${-scrollPosition}px)`,
transition: isDragging ? "none" : "transform 0.1s",
flexDirection: isHorizontal ? "row" : "column",
}}
>
{items.map((item, index) => {
// 判断是否是整数刻度
const isMajor = Number.isInteger(item);
const getTickClass = (item: number): string => {
const isHalf = !isMajor && Math.round(item * 10) % 10 === 5;
return clsx(
"bg-[#c3c7d5] relative",
isHorizontal
? isMajor
? "h-7"
: isHalf
? "h-6"
: "h-5"
: isMajor
? "w-7"
: isHalf
? "w-6"
: "w-5",
);
};
const selectedIndex = findNearestTickIndex(scrollPosition);
const distance = Math.abs(index - selectedIndex);
return (
<View
key={index}
className={clsx("bg-[#c3c7d5] relative", getTickClass(item))}
style={{
width: isHorizontal
? `${isMajor ? majorTickSize : minorTickSize}px`
: "w-1",
height: isHorizontal
? "h-1"
: `${isMajor ? majorTickSize : minorTickSize}px`,
}}
>
{isMajor && (
<Text
className={clsx(
"absolute font-medium text-base text-[#c3c7d5]",
isHorizontal
? "-top-3 left-0 -translate-x-1/2 -translate-y-[140%]"
: "-rotate-0 -left-12 top-0 -translate-y-1/2",
{
"text-[#b5b5b5] font-normal":
distance >= 1 && distance < 10,
"text-[#e6e6e6] font-normal": distance >= 10,
},
)}
>
{item}
</Text>
)}
</View>
);
})}
</View>
{/* 中心指示器 */}
<View
className={clsx(
"absolute bg-[#577cff]",
isHorizontal
? "left-1/2 -translate-x-1/2 h-7"
: "top-1/2 -translate-y-1/2 w-7",
)}
style={{
width: isHorizontal ? `${majorTickSize}px` : "",
height: isHorizontal ? "" : `${majorTickSize}px`,
}}
>
<Image
className={clsx(
"absolute w-3 h-3",
isHorizontal
? "left-1/2 -translate-x-1/2 -top-2/3"
: "-rotate-90 -translate-y-1/2 -left-2/3",
)}
src={triangle}
/>
</View>
</View>
</View>以上就是实现刻度尺的全部功能了。
一开始有考虑过使用虚拟滚动的方式来优化性能,但在深入设计后发现,虚拟滚动主要适用于长列表等线性滚动场景。而我们这个场景的特点是需要像素级的滚动、中心吸附、以及极高的精度控制。尤其是惯性滚动+吸附算法的实现,依赖所有刻度位置的可预知性和完整性。如果采用虚拟滚动,会导致吸附不准甚至刻度跳动的问题